How AI Is Transforming Appliance Repair & Predictive Maintenance
Artificial intelligence is quietly reshaping the way we diagnose and care for the machines that keep our homes running—refrigerators, washers, dryers, dishwashers, ovens, and more. What began as simple error codes has evolved into sensor-rich devices, cloud analytics, and apps that can predict failures before they happen. For homeowners, that means fewer surprises; for technicians, faster, more accurate repairs; and for manufacturers, product lines that learn from real-world use.
Below, we break down how AI works in appliance repair today, what benefits you can expect, where the technology still falls short, and how to use it responsibly—especially if you prefer DIY troubleshooting.
What “AI” actually means in this context

“AI” in appliance repair isn’t a single tool. It’s a stack of capabilities that often work together:
- Machine-learning diagnostics: Algorithms compare your appliance’s live data (temperatures, motor current, vibration, water flow, cycle duration) to patterns learned from thousands of prior cases.
- Predictive maintenance: Time-series models (think: anomaly detection) estimate when a component is drifting out of spec so you can fix a small issue before it becomes a major failure.
- Natural-language assistants: Chatbots and guided workflows translate technical symptoms—“washer won’t spin; slight burning smell”—into likely causes and next steps.
- Computer vision: Cameras or phone photos can help identify part numbers, belt misalignment, or burnt connectors.
- Optimization & logistics: Software suggests the right parts to stock in a van, the best service route, and even optimal installation settings based on local water hardness or voltage stability.
Why this matters to homeowners

- Faster, clearer troubleshooting: Instead of deciphering cryptic error codes, an AI guide can map your symptom to a short list of likely culprits, each with a probability and a step-by-step check.
- Fewer unnecessary part swaps: Smarter fault isolation means fewer “let’s try this part” guesses. That saves time, money, and returns.
- Prevention, not just reaction: Predictive alerts—e.g., “dryer vent resistance rising; clean the duct to avoid an overheat shutdown”—reduce breakdowns and help appliances last longer.
- Energy and water savings: Optimized cycles and early leak detection cut utility costs and avoid damage.
How technicians benefit

- First-visit fix rates go up: Better triage means arriving with the right part.
- Standardized quality: AI playbooks capture expert judgment, making junior techs more effective without replacing senior know-how.
- Safer work: Algorithms can flag electrical anomalies or gas risks before a tech starts disassembly.
- Training on demand: Interactive guides and AR overlays help techs navigate unfamiliar models.
Smart diagnostics: from error codes to context
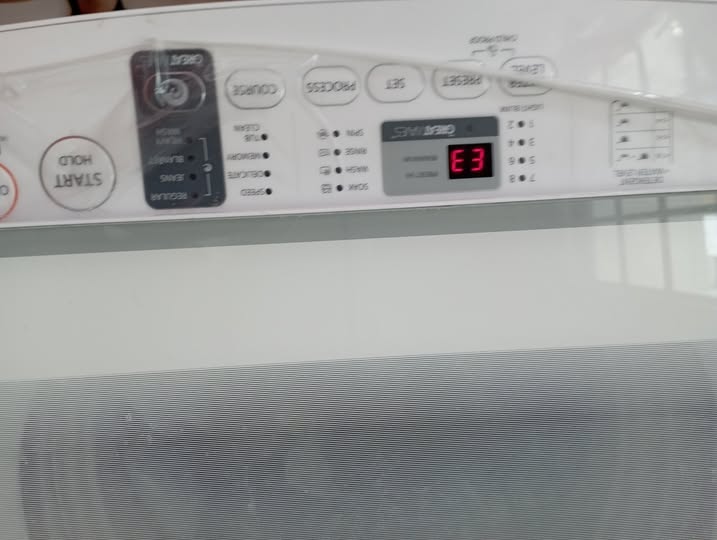

Traditional appliances expose a limited state (“E3: motor fault”). AI-enabled systems look at context: Did the fault occur under heavy load? After a power sag? With higher-than-normal vibration? That context narrows root causes dramatically. For example:
- Washers: ML models track motor current signatures to recognize worn bearings, stuck impellers, or unbalanced loads.
- Refrigerators: Temperature curves plus compressor duty cycles reveal low refrigerant, door-seal leakage, or an iced-over evaporator fan.
- Dishwashers: Pressure sensors and fill times spot inlet valve clogging versus flow meter failure.
Predictive maintenance: catching drift early

Components rarely fail instantly; they drift. An AI model can watch that drift—rising motor amperage, lengthening defrost cycles, incremental cycle retries—and alert you when the probability of failure crosses a threshold. The result: a scheduled fix rather than a weekend emergency.
Computer vision & robotics: niche but growing

While still emerging in residential contexts, computer vision can:
- Read worn label codes to identify the exact replacement part.
- Spot scorch marks or discoloration around connectors that indicate overheating.
- Verify belt alignment or pulley wear via a simple phone photo.
In service centers, light robotics assist with repetitive tasks—coil cleaning, screw sorting, or applying consistent torque—improving quality without replacing the human technician’s judgment.
Parts, pricing, and logistics: invisible AI that matters
Behind the scenes, optimization models predict which parts are worth stocking locally, the likely return rate on alternatives, and which suppliers meet delivery windows. Route planning reduces drive time and emissions. These small wins add up to faster repairs and lower costs.
Limitations and risks to keep in mind

- Data quality: Poor or missing sensor data will mislead even the best model. A clogged sensor is still a clogged sensor.
- Model bias toward common failures: If a rare fault isn’t well represented in training data, AI may “overconfidently” suggest a common—but wrong—fix.
- Connectivity dependence: Cloud-based diagnostics need a stable internet or a fallback.
- Privacy: Telemetry often includes device IDs, usage patterns, and error history. Understand what’s collected and how it’s stored.
- Right to repair: Some ecosystems lock diagnostics behind paywalls or proprietary tools. Transparency and access remain important policy discussions.
DIY with AI: how to troubleshoot responsibly

- Start with safety. Unplug or isolate power/gas before opening panels. If you smell gas, hear arcing, or see scorch marks, stop and call a professional.
- Use structured guides. Follow decision trees that ask for measurements (e.g., continuity, resistance, airflow) rather than jumping straight to part swaps.
- Document your steps. Photos and notes help you (or a pro) avoid repeats and mistakes.
- Validate with simple checks. Many “failures” are airflow, drainage, or installation issues.
- Know when to escalate. Refrigerant handling, sealed systems, and high-voltage power supplies are not DIY-friendly.
If you’re looking for clear, step-by-step resources, Appliance Rescue offers Expert Guides, Appliance Tips, and Troubleshooting Advice to help you understand issues and decide when to call a technician. Note that Appliance Rescue does not provide repair services—it’s an educational resource designed to empower homeowners with knowledge, not a dispatch center.
The human + AI workflow: augmented, not replaced
The best outcomes pair human judgment with machine pattern-matching. A seasoned technician recognizes context—pet hair clogging a vent, a child-lock setting, an odd rattle that only happens on spin. AI brings breadth: it remembers thousands of edge cases and can crunch data instantly. Together, they reduce misdiagnosis and downtime.
What’s next: from reactive to resilient homes
- Appliance “health scores” surfaced in your home app, much like a car’s maintenance monitor.
- Cross-device coordination: A washer delays spin to avoid overloading a shared circuit when the oven is in self-clean mode.
- Sustainability insights: Automated suggestions to extend lifespan—clean condenser coils now, replace a $15 gasket to save a compressor later.
- Open standards: More interoperable diagnostics so independent shops and DIYers can access the same high-quality guidance as OEM techs.
Getting help and staying informed
If you need clarity on a troubleshooting step, or you’re unsure whether an issue is safe to DIY, you can Contact us for guidance about the educational resources available. Again, Appliance Rescue is not a repair service; instead, the site provides curated advice to help you make informed, safe decisions and talk confidently with a local technician when needed.
Key takeaways
- AI is already improving accuracy, speed, and safety in appliance diagnostics.
- Predictive maintenance and context-aware analysis reduce surprise failures.
- Human expertise remains essential, especially for safety-critical work.
- Educational resources like Appliance Rescue help homeowners navigate issues—even though they do not offer repair services.
By understanding where AI shines (and where it doesn’t), homeowners and professionals can collaborate around better data, smarter tools, and, ultimately, longer-lasting appliances.